http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/cc300429.aspx
Category: Uncategorized
Array vs. ArrayList in ASP.NET
ArrayList and List Collection Types
.NET Framework 2.0
Other Versions
4 out of 6 rated this helpful – Rate this topic
An ArrayList or List object is a sophisticated version of an array. The ArrayList class and the List generic class provides some features that are offered in most System.Collections classes but are not in the Array class. For example:
•
The capacity of an Array is fixed, whereas the capacity of an ArrayList or a List is automatically expanded as required. If the value of the Capacity property is changed, the memory reallocation and copying of elements are automatically done.
•
ArrayList and List provide methods that add, insert, or remove a range of elements. In Array, you can get or set the value of only one element at a time.
•
A synchronized version of ArrayList or List is easy to create using the Synchronized method. The Array class leaves it up to the user to implement synchronization.
•
ArrayList and List provide methods that return read-only and fixed-size wrappers to the collection. Array does not.
On the other hand, Array offers some flexibility that ArrayList and List do not. For example:
•
You can set the lower bound of an Array, but the lower bound of an ArrayList or a List is always zero.
•
An Array can have multiple dimensions, while an ArrayList or a List always has exactly one dimension.
•
An Array of a specific type (other than Object) has better performance than an ArrayList because the elements of ArrayList are of type Object and, therefore, boxing and unboxing typically occur when storing or retrieving a value type. However, a List can have similar performance to an array of the same type if no reallocations are required; that is, if the initial capacity is a good approximation of the maximum size of the list.
Most situations that call for an array can use an ArrayList or a List instead; they are easier to use and, in general, have performance similar to an array of the same type.
Array is in the System namespace; ArrayList is in the System.Collections namespace; List is in the System.Collections.Generic namespace.
See Also
Reference
ArrayList
System.Collections
List
System.Collections.Generic
Array
Other Resources
Commonly Used Collection Types
Source: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-US/library/41107z8a(v=vs.80).aspx
Block Element Modifier Definition
Block Element Modifier (BEM) :
http://bem.github.com/bem-method/pages/beginning/beginning.en.html
SharePoint Hide Ribbon Actions
//Hide Save button on Ribbon, also being hidden by
SPRibbon ribbon = SPRibbon.GetCurrent(this.Page);
if (ribbon != null)
{
ribbon.TrimById(“Ribbon.ListForm.Edit.Commit.Publish”);
ribbon.TrimById(“Ribbon.ListForm.Edit.Actions.DeleteItem”);
ribbon.TrimById(“Ribbon.ListForm.Edit.Clipboard”);
ribbon.TrimById(“Ribbon.ListForm.Edit.SpellCheck”);
}
What’s New with ASP.NET 4.5 and Visual Studio
http://www.asp.net/vnext/overview/aspnet/whats-new#_Toc318097372
JavaScript Libraries
http://backbonejs.org/
http://handlebarsjs.com/
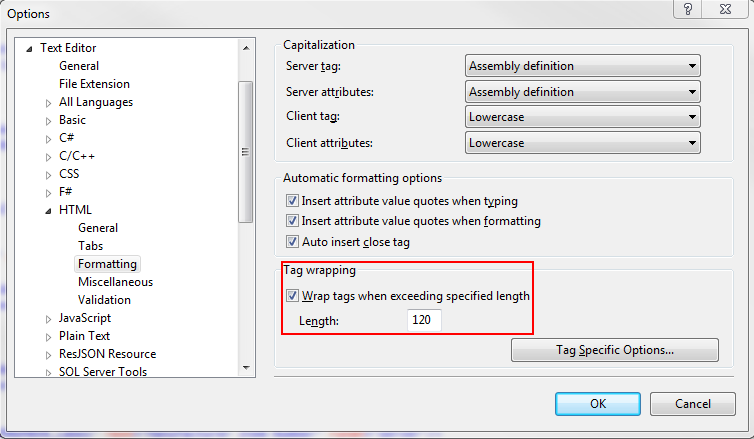
Visual Studio 2012 Set Line Wrap Length for HTML
CSS 3 and HTML 5 Button
[codesyntax lang=”vbnet”]
<%@ Page Language="VB" AutoEventWireup="false" CodeFile="Default.aspx.vb" Inherits="_Default" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
/*Button*/
.button {
display: inline-block;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
font: 14px/100% Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
font-weight:bold;
padding: .5em 2em .55em;
text-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.3);
-webkit-border-radius: .5em;
-moz-border-radius: .5em;
border-radius: .5em;
border-radius: 15px 15px 15px 15px;
-webkit-box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
-moz-box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
}
.button:hover {
text-decoration: none;
}
.button:active {
position: relative;
top: 1px;
}
/*Gradient*/
.orange {
color: #fef4e9;
border: solid 1px #da7c0c;
background: #f78d1d;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#faa51a), to(#f47a20));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #faa51a, #f47a20);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#faa51a', endColorstr='#f47a20');
}
.orange:hover {
background: #f47c20;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#f88e11), to(#f06015));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #f88e11, #f06015);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#f88e11', endColorstr='#f06015');
}
.orange:active {
color: #fcd3a5;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#f47a20), to(#faa51a));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #f47a20, #faa51a);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#f47a20', endColorstr='#faa51a');
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<a href="#" class="button orange">Orange</a>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
[/codesyntax]
Custom Field RequiredFieldValidator Highlighting
There was a great post here by Yoann. B that provided a great example in C# for highlighting RequireFieldValidators: http://blog.sb2.fr/post/2008/12/12/Custom-TextBox-Required-Field-Validator.aspx
I expanded the code to allow for border widths, and converted the code to VB.
[codesyntax lang=”vbnet”]
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Web.UI.WebControls
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.Web.UI
Imports System.Text
Namespace Validators
<DefaultProperty("Text")> _
<ToolboxData("<{0}:TextBoxRequiredFieldValidator runat=server></{0}:TextBoxRequiredFieldValidator>")> _
Public Class TextBoxRequiredFieldValidator
Inherits RequiredFieldValidator
#Region "Public Properties"
Public Property ErrorBackgroundColor() As Color
Get
If ViewState("ErrorBackgroundColor") Is Nothing Then
Return Color.LightGray
Else
Return DirectCast(ViewState("ErrorBackgroundColor"), Color)
End If
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Color)
ViewState("ErrorBackgroundColor") = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ErrorBorderColor() As Color
Get
If ViewState("ErrorBorderColor") Is Nothing Then
Return Color.Red
Else
Return DirectCast(ViewState("ErrorBorderColor"), Color)
End If
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Color)
ViewState("ErrorBorderColor") = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ErrorBorderWidth() As Unit
Get
If ViewState("ErrorBorderWidth") Is Nothing Then
Return Unit.Pixel(1)
Else
Return DirectCast(ViewState("ErrorBorderWidth"), Unit)
End If
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Unit)
ViewState("ErrorBorderWidth") = value
End Set
End Property
#End Region
#Region "Private Properties"
Private Property OriginalBackgroundColor() As Color
Get
If ViewState("OriginalBackgroundColor") Is Nothing Then
Return Color.LightGray
Else
Return DirectCast(ViewState("OriginalBackgroundColor"), Color)
End If
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Color)
ViewState("OriginalBackgroundColor") = value
End Set
End Property
Private Property OriginalBorderColor() As Color
Get
If ViewState("OriginalBorderColor") Is Nothing Then
Return Color.Red
Else
Return DirectCast(ViewState("OriginalBorderColor"), Color)
End If
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Color)
ViewState("OriginalBorderColor") = value
End Set
End Property
Private Property TextBoxToValidate() As TextBox
Get
Return m_TextBoxToValidate
End Get
Set(ByVal value As TextBox)
m_TextBoxToValidate = value
End Set
End Property
Private m_TextBoxToValidate As TextBox
#End Region
#Region "Protected Overrides Methods"
Protected Overrides Sub OnInit(ByVal e As EventArgs)
MyBase.OnInit(e)
Dim txt As TextBox = TryCast(Me.FindControl(MyBase.ControlToValidate), TextBox)
If txt IsNot Nothing Then
TextBoxToValidate = txt
OriginalBackgroundColor = TextBoxToValidate.BackColor
OriginalBorderColor = TextBoxToValidate.BorderColor
End If
End Sub
Protected Overrides Function EvaluateIsValid() As Boolean
Dim bIsValid As [Boolean] = False
Dim Value As [String] = MyBase.GetControlValidationValue(MyBase.ControlToValidate)
If [String].IsNullOrEmpty(Value) Then
If TextBoxToValidate IsNot Nothing Then
TextBoxToValidate.BackColor = ErrorBackgroundColor
TextBoxToValidate.BorderColor = ErrorBorderColor
bIsValid = False
End If
Else
If TextBoxToValidate IsNot Nothing Then
TextBoxToValidate.BackColor = OriginalBackgroundColor
TextBoxToValidate.BorderColor = OriginalBorderColor
bIsValid = True
End If
End If
Return bIsValid
End Function
Protected Overrides Sub OnPreRender(ByVal e As EventArgs)
MyBase.OnPreRender(e)
If Page.ClientScript.IsClientScriptBlockRegistered("ValidationScript") Then
Return
End If
Dim ControlToValidateClientId As [String] = MyBase.GetControlRenderID(MyBase.ControlToValidate)
Dim Script As New StringBuilder()
Script.Append("<script language=""javascript"">")
Script.Append("function RequiredFieldValidatorEvaluateIsValid(val) {")
Script.Append(" var value = ValidatorGetValue(val.controltovalidate);")
Script.Append("if (value == '') {")
Script.Append("document.getElementById(val.controltovalidate).style.backgroundColor = '$$BGCOLOR$$';")
Script.Replace("$$BGCOLOR$$", ColorTranslator.ToHtml(ErrorBackgroundColor))
Script.Append("document.getElementById(val.controltovalidate).style.borderColor = '$$BRCOLOR$$';")
Script.Replace("$$BRCOLOR$$", ColorTranslator.ToHtml(ErrorBorderColor))
Script.Append("document.getElementById(val.controltovalidate).style.borderWidth = '$$BRWIDTH$$';")
Script.Replace("$$BRWIDTH$$", ErrorBorderWidth.ToString)
Script.Append("return false; }")
Script.Append("else {")
Script.Append("document.getElementById(val.controltovalidate).style.backgroundColor = '$$ORIG_BGCOLOR$$';")
Script.Replace("$$ORIG_BGCOLOR$$", ColorTranslator.ToHtml(OriginalBackgroundColor))
Script.Append("document.getElementById(val.controltovalidate).style.borderColor = '$$ORIG_BRCOLOR$$';")
Script.Replace("$$ORIG_BRCOLOR$$", ColorTranslator.ToHtml(OriginalBorderColor))
Script.Append("return true;} }")
Script.Append("</script>")
Page.ClientScript.RegisterClientScriptBlock(Me.[GetType](), "ValidationScript", Script.ToString())
End Sub
#End Region
End Class
End Namespace
[/codesyntax]
Here is the usage of the Overload.
You must register the custom control on the page, include the “Assembly” attribute if from outside your project.
[codesyntax lang=”vbnet”]
<%@ Register TagPrefix="MyCtrl" Namespace="Validators" %>
[/codesyntax]
The control is used just like the regular required field validator.
[codesyntax lang=”vbnet”]
<myctrl:textboxrequiredfieldvalidator ID="valid1" runat="server" ControlToValidate="TextBox1" ErrorBackgroundColor="Red" ErrorBorderColor="Red" ErrorBorderWidth="2" SetFocusOnError="true"></myctrl:textboxrequiredfieldvalidator>
[/codesyntax]
Status Codes and MIME Types
text Textual information. Subtypes include plain, html, and xml.
image Image data. Subtypes are defined for two widely used image formats,
jpeg and gif, and other subtypes exist as well.
audio Audio data. Requires an audio output device (such as a speaker or headphones)
for the contents to be heard. An initial subtype, basic, is defined
for this type.
video Video data. The subtype mpeg is often used. Typically, videos are not
transferred directly, but are read from an embedded object, such as a
JavaScript or Adobe Flash object.
application Any binary data. The subtype octet-stream is typically used.